When building or purchasing a home, one of the most critical design choices you’ll face is deciding on the type of roof.
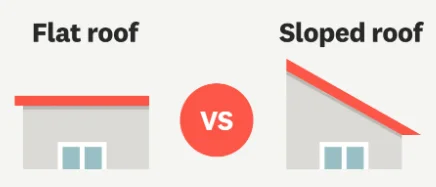
The two most common options are flat roofs and sloped (or normal) roofs. Each type offers unique advantages and drawbacks, and the decision will impact your home’s aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Flat roofs in Kenya have become a new trend and have taken shape recently. If you visit areas like Kitengela, Ngong, and Ongata Rongai, several residential properties adopt flat roof models.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the differences between flat and sloped roofs, their pros and cons, and the factors to consider when choosing the right roof for your home.
The difference between a Flat Roof and a Sloped Roof
What is a Flat Roof?

A flat roof, as the name suggests, is a roof with a nearly horizontal surface.
Though they appear flat, they typically have a slight slope (around 1-10 degrees) to allow for water drainage.
Flat roofs are commonly found in modern and commercial architecture, but they are also making their way into residential design, especially in urban and contemporary homes.
What is a Sloped (Normal) Roof?
A sloped or pitched roof is the more traditional roofing style, characterized by its angled surface. The roof’s slope can vary significantly, from a gentle incline to a steep pitch, depending on the architectural style.
Sloped roofs are commonly seen in suburban homes and are often associated with more conventional architectural styles like Colonial, Ranch, and Cape Cod homes.
Pros and Cons of Flat Roofs
Flat roofs offer a range of benefits, but they also have their share of drawbacks. Here’s a closer look at the pros and cons:
Advantages of Flat Roofs
- Modern Aesthetic Flat roofs are commonly associated with modern, minimalist architectural styles. If you want your home to have a sleek, contemporary look, a flat roof may be the best choice. Flat roofs are often found in homes with open floor plans and large windows, contributing to a clean, geometric design.
- Cost-Effective Flat roofs are typically less expensive to construct than sloped roofs due to the lower complexity of the design. Since fewer materials are required, and installation is generally faster, you can save on both labor and material costs.
- Usable Space One of the biggest advantages of a flat roof is the potential for additional usable space. A flat roof can be turned into a rooftop garden, patio, or even an outdoor living area. This is particularly useful in urban settings where yard space may be limited. Solar panels or HVAC systems can also be installed on a flat roof more easily.
- Easier Access Maintenance and repairs are often easier and safer with a flat roof due to its accessibility. You can walk on a flat roof with little to no risk, making it simpler to clean gutters, inspect for damage, or make necessary repairs.
Disadvantages of Flat Roofs
1. Drainage Issues
One of the biggest disadvantages of flat roofs is their poor drainage capabilities. Unlike sloped roofs, which naturally allow rain and snow to slide off, flat roofs require a carefully designed drainage system to prevent water pooling.
Without proper drainage, water can accumulate on the surface, leading to leaks, structural damage, and mold growth.
2. Higher Maintenance
Flat roofs generally require more frequent maintenance than sloped roofs.
The risk of water damage, combined with the potential for debris buildup, means that homeowners with flat roofs need to be vigilant about routine inspections and repairs.
3. Shorter Lifespan
Due to their increased exposure to water and the elements, flat roofs tend to have a shorter lifespan than sloped roofs.
While advancements in roofing materials have improved the durability of flat roofs, they still typically last between 10-20 years, compared to the 30-50 years that a well-maintained sloped roof can offer.
4. Limited Aesthetics
Flat roofs are typically constructed using materials like rubber, PVC, or modified bitumen, which may not be as aesthetically pleasing or as durable as the shingles, tiles, or metal often used in sloped roofs.
Pros and Cons of Sloped Roofs
Sloped roofs have been the standard choice for homes for centuries, and they offer several clear benefits. However, they come with some downsides as well.
Advantages of Sloped Roofs
1. Effective Drainage
The most significant advantage of a sloped roof is its excellent drainage capability.
Rain, snow, and debris naturally slide off the roof, reducing the risk of water damage and leaks. This makes sloped roofs ideal for regions with heavy rainfall or snowfall.
2. Durability and Longevity
Sloped roofs tend to last longer than flat roofs, primarily because they are better equipped to handle the elements.
The steep pitch helps shed water and snow more efficiently, which can extend the roof’s lifespan. With proper maintenance, a sloped roof can last several decades.
3. Variety of Roofing Materials
Sloped roofs offer more flexibility when it comes to choosing roofing materials. You can choose from a wide range of options, including asphalt shingles, metal, clay tiles, and slate.
This allows homeowners to select materials that best suit their aesthetic preferences and climate needs.
4. Energy Efficiency
A sloped roof can provide better insulation and energy efficiency, especially in colder climates.
The steep pitch allows for more space between the roof and the living area, which can be used for insulation. This helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
5. Traditional Appeal
Sloped roofs are associated with more traditional, cozy, and timeless architectural styles. If you prefer a classic or rustic look for your home, a sloped roof may be a better fit for your aesthetic vision.
Cons of Sloped Roofs
1. Higher Construction Costs
Sloped roofs are generally more expensive to build due to their complexity. They require more materials, specialized labor, and longer installation times.
While the upfront cost is higher, the long-term durability and reduced maintenance needs may offset these initial expenses.
2. Limited Usable Space
Unlike flat roofs, sloped roofs don’t offer any additional usable space. While an attic can provide storage, it doesn’t offer the same potential for outdoor living areas or gardens as a flat roof does.
3. Difficult Access
Sloped roofs are more challenging and dangerous to access for maintenance and repairs. Homeowners may need to hire professional roofers to perform routine inspections, clean gutters, or address any issues that arise, which can increase maintenance costs.
4. Susceptibility to Wind Damage
In areas prone to high winds or hurricanes, sloped roofs can be more susceptible to wind damage. The slope of the roof can catch the wind, potentially causing shingles or tiles to lift or tear off.
However, the use of wind-resistant materials and proper installation can mitigate this risk.
Factors to Consider when Choosing Between Flat and Sloped Roof
When deciding between a flat or sloped roof for your home, several factors should guide your choice:
1. Climate
The climate in which you live is one of the most important considerations. If you live in an area with heavy rainfall or snowfall, a sloped roof may be a better choice due to its superior drainage capabilities.
Flat roofs, on the other hand, can work well in drier climates or urban areas where space is at a premium.
2. Aesthetic Preference
The look of your home is another significant factor. If you’re aiming for a modern, minimalist design, a flat roof may be the perfect fit. For those who prefer a more traditional or classic aesthetic, a sloped roof will likely be more suitable.
3. Budget
Your budget will play a role in your decision as well. Flat roofs are generally more affordable to construct, but they may require more maintenance over time.
Sloped roofs have a higher initial cost, but they tend to last longer and require fewer repairs.
4. Maintenance
Consider how much time and effort you’re willing to invest in maintaining your roof. Flat roofs typically need more frequent inspections and repairs, while sloped roofs require less maintenance but may be more difficult and costly to access when issues arise.
5. Energy Efficiency
If energy efficiency is a priority, you may want to consider how each roof type impacts your home’s heating and cooling.
Sloped roofs can provide better insulation and ventilation, particularly in colder climates, while flat roofs can be easier to outfit with solar panels in sunny areas.
6. Future Plans
Think about your long-term plans for the home. If you want the option to expand your living space with a rooftop patio or garden, a flat roof may be the better choice.
If you’re focused on long-term durability and minimal maintenance, a sloped roof might be the way to go.
Final Word
The choice between a flat roof and a sloped roof depends on a variety of factors, including your budget, aesthetic preferences, and the climate in which you live.
Flat roofs offer a modern aesthetic and additional usable space but require more maintenance and are prone to drainage issues.
Sloped roofs provide superior drainage, durability, and energy efficiency, but come with higher upfront costs and more limited design flexibility.
Ultimately, the best choice will depend on your personal needs and priorities. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each option, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your vision for your home and its future.